Published on 2025-06-29T19:04:03Z
What is Data Segmentation? Examples for Campaign Tracking & Analytics
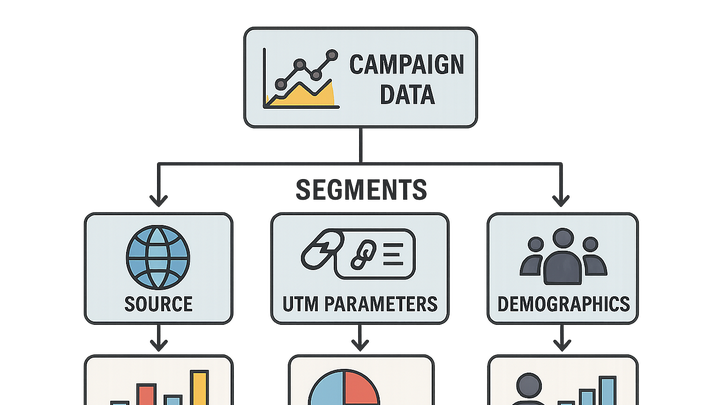
Data segmentation is the process of dividing marketing data into distinct groups to analyze performance and target specific audiences. In campaign tracking & analytics, segmentation helps marketers isolate subsets of traffic by attributes such as source, behavior, or demographics, enabling more precise insights and tailored strategies. Tools like Plainsignal provide cookie-free analytics allowing segmentation by UTM parameters, device type, or geographical region, while UTM Guru simplifies tag creation to ensure consistent segment tracking across campaigns. By breaking down aggregate data, segmentation reveals hidden patterns, optimizes budget allocation, and improves conversion rates. It supports A/B testing, personalized messaging, and churn analysis by focusing on the segments that matter most for growth. Well-defined segments drive efficient resource use, deeper insights, and better ROI measurement for marketing campaigns.
Data segmentation
Dividing marketing data into distinct groups (by source, behavior, demographics) for targeted analysis and better campaign insights.
Why Data Segmentation Matters
Segmenting data enables marketers to move beyond aggregate metrics and understand the unique behaviors and value of different audience groups. This leads to more informed decision-making, optimized campaign performance, and personalized marketing strategies. By focusing on specific segments, teams can allocate budgets more efficiently, identify high-value audiences, and measure ROI more accurately.
-
Enhances insight granularity
Segmentation breaks down aggregated metrics into specific groups, revealing performance differences that would be hidden in overall averages.
-
Optimizes campaign performance
By analyzing segments individually, marketers can allocate budget to high-performing audiences and tailor messaging to each group’s preferences.
-
Supports personalized marketing
Segmentation enables personalized content and offers, increasing engagement and conversion rates by delivering relevant experiences.
-
Improves roi measurement
Isolating segments helps attribute conversions and revenue to the right channels, providing clearer ROI calculations for each segment.
Types of Segmentation in Campaign Analytics
Campaign analytics commonly employs multiple segmentation dimensions to dissect traffic and user behavior. Each type offers a unique lens through which marketers can evaluate performance and optimize strategies.
-
Source segmentation
Divides traffic based on origin, such as organic, paid, referral, email, or social channels.
- Utm source:
Uses the utm_source parameter to identify the traffic origin.
- Referral domains:
Groups visits by the referring website’s domain.
- Utm source:
-
Behavioral segmentation
Focuses on user actions like page views, session duration, click patterns, and conversion events.
- Page engagement:
Segments users by pages viewed or time spent on site.
- Event tracking:
Uses custom events (e.g., form submissions) to define segments.
- Page engagement:
-
Demographic segmentation
Categorizes users by age, gender, location, device type, or language.
- Geo location:
Segments traffic based on geographic region or city.
- Device type:
Breaks down data by desktop, mobile, or tablet users.
- Geo location:
-
Cohort segmentation
Groups users by shared characteristics or behaviors during a defined period, useful for retention and churn analysis.
- Acquisition cohorts:
Users grouped by signup or purchase date.
- Behavioral cohorts:
Users grouped by similar in-app actions or campaign responses.
- Acquisition cohorts:
How to Implement Data Segmentation with SaaS Tools
A step-by-step guide to setting up segmentation using popular SaaS products like PlainSignal and UTM Guru.
-
Using plainsignal for cookie-free segmentation
PlainSignal provides simple, privacy-compliant analytics that support segmentation by UTM parameters, referrer, and custom tags. To integrate PlainSignal:
<link rel=\"preconnect\" href=\"//eu.plainsignal.com/\" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do=\"yourwebsitedomain.com\" data-id=\"0GQV1xmtzQQ\" data-api=\"//eu.plainsignal.com\" src=\"//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js\"></script>Once installed, use the PlainSignal dashboard to build segments based on URL parameters, device type, or regions.
- Segment builder:
Define segmentation rules in the PlainSignal UI using filters like utm_campaign, region, or device.
- Filter and compare:
Apply multiple filters simultaneously to compare different audience segments.
- Segment builder:
-
Using utm guru for utm-based segmentation
UTM Guru simplifies the creation and management of UTM parameters, ensuring consistent tagging across campaigns. Steps to generate and apply UTM tags:
- Open UTM Guru or its Chrome extension.
- Fill out campaign parameters: source, medium, campaign name, term, content.
- Generate the URL and save it for future reference.
- Apply the tagged URL in emails, ads, or social posts. In your analytics tool, filter or segment data using the utm_campaign, utm_source, and utm_medium parameters created by UTM Guru.
- Tag creation:
Use UTM Guru’s builder to input consistent naming conventions for source, medium, and campaign.
- Campaign management:
Save and organize generated URLs in UTM Guru for reuse and reporting.
- Segment filtering:
In your analytics dashboard, apply filters on utm parameters to view specific campaign performance.
Best Practices for Effective Segmentation
Apply proven best practices to ensure your segmentation strategy yields accurate insights and actionable results.
-
Define clear segment criteria
Use measurable and relevant attributes to ensure segments are meaningful and actionable.
- Single variable focus:
Start with one dimension (e.g., utm_source) before combining multiple filters.
- Avoid over-segmentation:
Too many small segments can lead to data sparsity and skewed insights.
- Single variable focus:
-
Maintain consistent naming conventions
Standardize UTM and tag names to avoid duplication and confusion across campaigns.
- Lowercase tags:
Use lowercase letters to prevent case-sensitive mismatches.
- Underscores vs. hyphens:
Choose one delimiter and apply it consistently.
- Lowercase tags:
-
Regularly review and update segments
Assess segment performance and refine criteria based on evolving marketing goals and data trends.
- Periodic audits:
Schedule monthly or quarterly reviews to validate segment relevance.
- Merge or retire segments:
Consolidate underperforming segments to streamline analysis.
- Periodic audits:
-
Ensure data privacy and compliance
Respect user privacy and adhere to regulations like GDPR and CCPA when segmenting data.
- Anonymize user data:
Avoid collecting personally identifiable information without consent.
- Cookie-free options:
Leverage tools like PlainSignal for privacy-first analytics.
- Anonymize user data: