Published on 2025-06-29T18:00:02Z
What is Paid Search? Examples and Best Practices in Campaign Tracking & Analytics
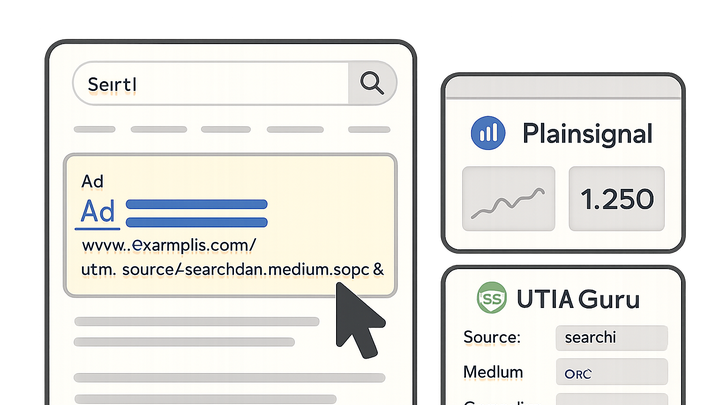
Paid Search, also known as search engine marketing (SEM), is a form of digital advertising where marketers bid on keywords to display ads in search engine results pages (SERPs). Advertisers pay each time a user clicks on their ad, following a cost-per-click (CPC) pricing structure. In campaign tracking and analytics, accurately measuring clicks, conversions, and return on ad spend (ROAS) is vital for optimizing performance. Marketers typically append UTM parameters to their ad URLs to capture detailed campaign data in analytics platforms. Tools like Plainsignal offer a cookie-free analytics solution for privacy-conscious tracking, while UTM Guru simplifies building, generating, and managing UTM-tagged URLs through its web app and Chrome extension. By integrating these tools, businesses can effortlessly attribute paid search traffic, evaluate ROI, and refine keyword targeting and ad creatives to maximize conversion rates.
Paid search
Paid Search: advertisers bid on keywords, pay per click on search ads, and use UTM parameters and analytics tools to track performance.
Overview of Paid Search
Paid Search, also known as search engine marketing (SEM), is a form of digital advertising where marketers bid on keywords to display ads in search engine results pages (SERPs). This model uses a cost-per-click (CPC) structure, charging advertisers each time a user clicks an ad. Paid Search allows precise targeting by keyword, location, device, and audience demographics. It is essential for driving qualified traffic, capturing high-intent leads, and maximizing return on ad spend (ROAS).
-
Definition
Paid Search refers to placing ads on SERPs through keyword bidding. Advertisers set budgets, bids, and ad creatives to reach users actively searching for related terms.
-
Key components
Understanding the building blocks of Paid Search is critical for campaign success.
- Ad auction & bidding:
Search engines run auctions in real-time to determine which ads appear and in which order, based on bids and quality.
- Keywords & match types:
Advertisers select keywords and match types (broad, phrase, exact) to control when ads are triggered.
- Ad creatives & extensions:
Text, responsive, or shopping ads include headlines, descriptions, and extensions like sitelinks for enhanced visibility.
- Landing pages & conversions:
Well-optimized landing pages ensure that clicks lead to desired actions, such as purchases or sign-ups.
- Ad auction & bidding:
Tracking Paid Search Campaigns
Accurate tracking is the backbone of successful Paid Search campaigns. By appending UTM parameters to ad URLs and using analytics tools—such as PlainSignal for cookie-free analytics and UTM Guru for streamlined UTM generation—marketers can collect granular data, attribute conversions, and optimize performance.
-
Utm parameters
UTM parameters are tags added to URLs to capture campaign metadata in analytics platforms.
- Utm_source:
Identifies the origin of traffic (e.g., google, bing).
- Utm_medium:
Specifies the marketing medium (e.g., cpc).
- Utm_campaign:
Denotes the campaign name or identifier.
- Utm_term:
Tracks paid keywords triggering the ad.
- Utm_content:
Differentiates A/B tests or ad variations.
- Utm_source:
-
Using plainsignal for analytics
PlainSignal offers a privacy-centric, cookie-free analytics solution ideal for modern Paid Search tracking. Integrate PlainSignal with the following code snippet:
- Integration code:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
- Integration code:
-
Generating utms with utm guru
UTM Guru simplifies building, storing, and managing UTM-tagged URLs through its web app and Chrome extension, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Best Practices and Real-World Examples
Implementing best practices and reviewing real-world examples helps optimize Paid Search campaigns. Consistent naming, regular performance reviews, and iterative testing are key to maximizing ROI.
-
Campaign structure & naming
Maintain clear, consistent naming conventions for campaigns, ad groups, and UTMs to simplify reporting and analysis.
- Descriptive campaign names:
Include platform, objective, and date (e.g., “google_cpc_spring_sale_2025”).
- Utm consistency:
Use standardized lowercase and hyphens to avoid data fragmentation in analytics.
- Descriptive campaign names:
-
Monitoring & optimization
Regularly analyze Paid Search metrics using PlainSignal dashboards to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Key metrics:
Focus on CTR, CPC, conversion rate, and ROAS to gauge performance.
- A/b testing:
Test ad copy, bid strategies, and landing pages to discover top-performing elements.
- Key metrics:
-
Real-world example
A Google Ads campaign targeting running shoes uses the following UTM setup and PlainSignal tracking to measure success:
- Example utm url:
https://example.com/landing?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=running_shoes_spring - Analytics outcome:
PlainSignal reports show a 4.2% CTR, $0.75 CPC, and a 3.8% conversion rate, guiding budget reallocation to high-performing keywords.
- Example utm url: