Published on 2025-06-29T18:38:21Z
What is Affiliate Marketing? Examples for Affiliate Marketing
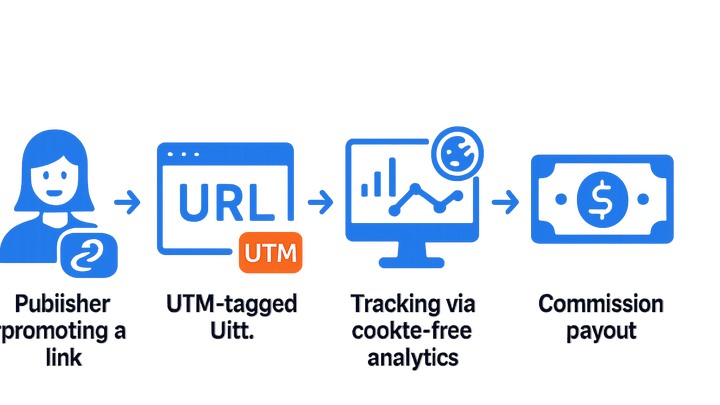
Affiliate Marketing is a performance-based marketing strategy where businesses (advertisers) reward third-party partners (affiliates) for driving traffic or sales through the affiliates’ promotional efforts. Within the campaign tracking & analytics industry, affiliate marketing relies heavily on accurate attribution methods, such as UTM parameters and cookieless tracking, to measure the success of individual affiliates and channels. Effective tracking allows marketers to optimize commission structures, identify top-performing partners, and allocate budgets more efficiently. Modern analytics solutions, like Plainsignal, offer simple, privacy-focused tracking without cookies, while tools like UTM Guru streamline the creation and management of UTM-tagged URLs for affiliate campaigns. By integrating these tools into your affiliate strategy, you can ensure transparency, improve ROI, and maintain compliance with data privacy regulations. Affiliate marketing remains a scalable, cost-effective channel for acquiring new customers and increasing brand awareness.
Affiliate marketing
Performance-based marketing where affiliates earn commissions by driving tracked traffic or sales, using UTM tags and advanced attribution.
Why Affiliate Marketing Matters
Affiliate marketing is a scalable, performance-driven channel that helps businesses acquire new customers with minimal upfront costs. Affiliates only earn commissions for measurable results, aligning incentives between advertisers and partners. This cost-per-action model reduces financial risk while maximizing ROI. Advanced tracking and analytics enable precise measurement of affiliate contributions, empowering marketers to optimize budgets and strategies in real time.
-
Performance-based growth
Advertisers pay affiliates based on specific actions (clicks, leads, or sales), ensuring marketing spend directly correlates with results.
-
Cost efficiency
With no upfront ad spend, businesses can scale affiliate programs rapidly, only paying for actual conversions achieved by partners.
Core Components of Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate programs consist of several key players and elements that work together to drive and track performance. Understanding these components is crucial for designing an effective affiliate strategy and selecting the right tracking infrastructure.
-
Advertiser (merchant)
The brand or business that offers products or services and pays commissions to affiliates for driving desired actions.
-
Affiliate (publisher)
Third-party partners or content creators who promote the advertiser’s offers through various channels like blogs, social media, or email.
-
Affiliate network or platform
Intermediary platforms that facilitate tracking, reporting, and payment between advertisers and affiliates.
-
Commission model
The structure by which affiliates are compensated, commonly cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-lead (CPL), cost-per-acquisition (CPA), or revenue share.
- Cpc:
Pay per click on affiliate links.
- Cpl:
Pay per qualified lead generated.
- Cpa:
Pay when a sale or specific action is completed.
- Revenue share:
Affiliate receives a percentage of the sale value.
- Cpc:
Tracking Affiliate Marketing Campaigns
Accurate tracking is vital to measure affiliate performance, attribute revenue correctly, and prevent fraud. Modern affiliate tracking combines URL parameters, cookies, and server-side methods to capture user interactions from click to conversion.
-
Utm parameters
Adding UTM tags to affiliate links helps analytics platforms attribute traffic and conversions to specific affiliates and campaigns.
- Utm_source:
Identifies the affiliate or referral partner.
- Utm_medium:
Specifies the marketing medium, often set to ‘affiliate.’
- Utm_campaign:
Describes the promotion or campaign name.
- Utm_term & utm_content:
Optional parameters for granular targeting or creative differentiation.
- Utm_source:
-
Cookieless analytics
With increasing privacy regulations and browser restrictions, cookieless solutions like PlainSignal enable tracking clicks and conversions without relying on third-party cookies.
-
Attribution models
Different models determine how credit is assigned to affiliates, including first-click, last-click, and multi-touch attribution to reflect the customer journey accurately.
- Last-click attribution:
Gives all credit to the final click before conversion.
- First-click attribution:
Attributes the conversion to the initial click.
- Multi-touch attribution:
Distributes credit across multiple touchpoints in the customer journey.
- Last-click attribution:
SaaS Tools for Affiliate Marketing Tracking
Leveraging specialized SaaS solutions simplifies campaign setup, tracking, and reporting. Below are examples of two powerful tools for affiliate analytics and UTM management.
-
Plainsignal
A cookie-free analytics platform that tracks affiliate clicks and conversions with a simple script. Ideal for privacy-focused campaigns.
- Installation snippet:
Add the following code to your site’s
<head>to enable tracking:<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
- Installation snippet:
-
Utm guru
A UTM builder and generator that helps affiliates create, save, and manage UTM-tagged URLs. Available as a web app and Chrome extension for quick campaign-tracking setup.
Best Practices and Tips
To maximize affiliate marketing success, follow these best practices for accurate tracking, partner management, and compliance.
-
Standardize utm naming
Use consistent naming conventions for UTM parameters to ensure data cleanliness and easy reporting.
-
Monitor affiliate performance regularly
Review key metrics like click-through rates, conversion rates, and average order value to identify top partners and optimize commissions.
-
Ensure privacy compliance
Choose cookieless or server-side tracking solutions and provide clear disclosures to comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations.
-
Fraud detection
Implement fraud monitoring to detect suspicious patterns like multiple conversions from the same user or location.