Published on 2025-06-29T18:20:49Z
What is Multi-Channel Attribution? Examples of Multi-Channel Attribution
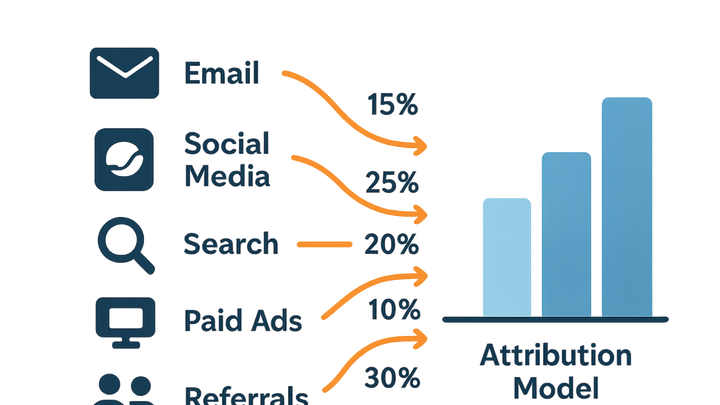
Multi-Channel Attribution is the practice of assigning credit for conversions across the various touchpoints a customer interacts with before completing a desired action. Rather than attributing value only to the first or last interaction, it evaluates the relative impact of channels like organic search, paid ads, social media, email, and referrals. This approach requires consistent UTM tagging, robust tracking scripts, and analytics tools that can stitch together disparate data sources. SaaS solutions such as plainsignal (a cookie-free analytics platform) and utmguru.com (a UTM builder and manager) streamline implementation and ensure reliable data collection. By providing a holistic view of the customer journey, Multi-Channel Attribution empowers marketers to optimize budget allocation, improve ROI, and make data-driven decisions, while also navigating challenges around privacy, data consistency, and model selection. Implementing Multi-Channel Attribution involves selecting appropriate attribution models, handling data integration, and regularly auditing campaign setups to maintain accuracy.
Multi-channel attribution
Assign credit to multiple marketing touchpoints across channels to optimize budget and understand their impact on conversions.
Why Multi-Channel Attribution Matters
Multi-Channel Attribution provides a holistic view of how different marketing channels contribute to conversions, enabling more informed budget decisions and better ROI analysis.
-
Holistic customer journey insights
By tracking all touchpoints—from initial awareness to final conversion—marketers gain a complete picture of user behavior across channels.
-
Optimized marketing spend
Understanding the impact of each channel allows for reallocating budget to the most effective tactics, reducing wasted ad spend.
-
Improved roi measurement
Attributing partial credit to secondary interactions yields more accurate ROI calculations compared to single-touch models.
Common Attribution Models
Several models exist to assign credit across touchpoints, each with its own trade-offs and use cases.
-
First-touch attribution
Assigns 100% of conversion credit to the first interaction a user has with your brand. Useful for awareness campaigns but ignores later influences.
-
Last-touch attribution
Gives all credit to the final touchpoint before conversion. Simple to implement but overlooks earlier engagements.
-
Linear attribution
Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints. Balances recognition but may undervalue key moments.
-
Time-decay attribution
Allocates more credit to touchpoints closer to conversion. Highlights recent interactions but downplays early awareness efforts.
-
Position-based (u-shaped) attribution
Credits 40% each to the first and last interactions and divides the remaining 20% among middle touchpoints. Balances awareness and conversion influence.
-
Data-driven attribution
Uses statistical algorithms and machine learning to assign credit based on the actual impact of each touchpoint. Requires sufficient data volume to be reliable.
Implementing Multi-Channel Attribution with SaaS Tools
You can leverage specialized SaaS platforms to streamline UTM tagging, data collection, and analysis without managing complex infrastructure.
-
Utm tagging with utmguru.com
Use utmguru.com’s UTM builder and Chrome extension to generate, manage, and store consistent UTM parameters for all your campaigns. This ensures uniform tagging and reduces errors.
- Consistent parameter management:
Store and reuse UTM templates in UTMGuru to maintain standardized naming conventions across teams.
- Chrome extension:
Generate and copy UTM URLs directly from your browser as you browse or launch campaigns.
- Consistent parameter management:
-
Cookie-free tracking with plainsignal
Integrate PlainSignal’s simple JavaScript snippet to collect pageviews and events without relying on cookies, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
- Integration snippet:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> - Event configuration:
Define custom events and conversion goals in the PlainSignal dashboard to capture critical user interactions beyond pageviews.
- Integration snippet:
-
Data analysis and visualization
Combine UTM parameter data from UTMGuru with event data from PlainSignal in BI tools or analytics dashboards (e.g., Google Data Studio) to build multi-channel attribution reports.
Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing Multi-Channel Attribution involves navigating data consistency, model selection, and privacy considerations. Adhering to best practices helps maintain data integrity and actionable insights.
-
Data consistency
Inconsistent or missing UTM tags lead to gaps and misattribution. Establish strict naming conventions and audit tags regularly.
-
Managing channel overlap
Channels like social and paid search often overlap in a user’s journey. Use unique UTM values and custom event tracking to distinguish similar interactions.
-
Choosing the right model
Tailor your attribution model to your business goals and sales cycle complexity. Test multiple models and compare results to find the optimal approach.
-
Privacy and compliance
With evolving privacy regulations reducing cookie availability, consider cookie-free tools like PlainSignal and ensure UTM practices respect user consent.
Pro Tips for Effective Attribution
To maximize the value of your attribution efforts, follow these advanced recommendations and regularly refine your approach.
-
Leverage custom reporting
Build custom attribution reports in your analytics platform to visualize touchpoint paths and weighted credit across channels.
-
Regularly audit campaign setup
Perform periodic checks on UTM tags, script implementations, and data pipelines to identify and correct issues before they skew analysis.
-
Integrate offline and crm data
Enrich your digital attribution data by importing sales, CRM, and call-tracking information to capture touchpoints outside digital channels.